blog
5 Suggestions to Upgrade your OpenTofu/Terraform & AWS Development Experience
Tools and scripts to help you reclaim your focus and speed up your workflow.
Read More

A roadmap for ensuring post-migration stability, security, and performance.
March 21, 2025
Author: Travis Langhals, Principal Architect at UTurn Data Solutions
Cloud migration is often seen as the finish line. In reality, it’s just the starting point. Moving workloads to AWS is a significant milestone, but ensuring long-term success requires ongoing optimization.
Many organizations encounter unexpected cost overruns, performance issues, and security vulnerabilities in the weeks following a migration. Without a structured plan, the benefits of cloud adoption—scalability, flexibility, and cost savings—can be diminished by poor management practices.
There are five key areas organizations must focus on after migration to ensure a smooth transition:
Let’s take a deeper dive into each one.
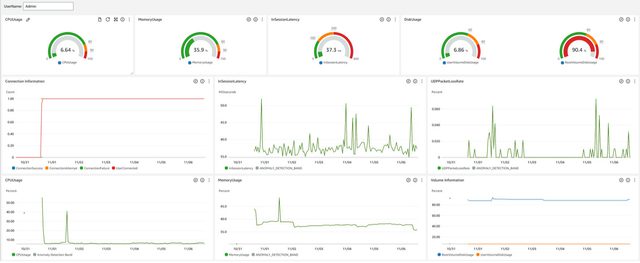
Once workloads are running in AWS, real-time monitoring is essential to track system health, prevent performance bottlenecks, and optimize resource utilization.
Key actions in the first 90 days:
Organizations that actively monitor performance early in the post-migration phase can prevent resource waste and performance degradation before they become larger issues.
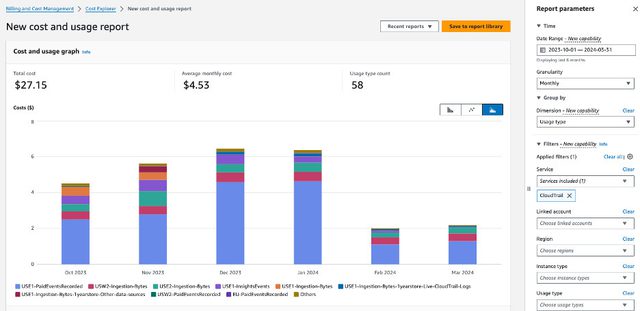
Without active management, AWS costs can escalate quickly. Many organizations assume cloud expenses will naturally decrease due to scalability, but in reality, inefficient resource allocation and lack of governance can lead to unnecessary spending.
Steps to control costs:
A proactive approach to cost governance prevents financial surprises and ensures AWS adoption remains economically viable.
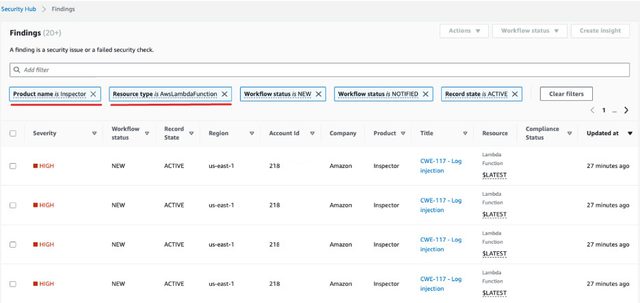
Understanding the AWS shared responsibility model is essential for ensuring a strong security posture of migrated applications. AWS provides robust foundational infrastructure security along with extensive security capabilities and services, but customers remain responsible for securing their workloads, configurations, and data within the cloud environment. Without proper implementation of security controls on the customer side, misconfigured permissions and overlooked vulnerabilities can still pose significant risks despite AWS’s secure infrastructure.
Security priorities post-migration:
Addressing security early in the cloud journey reduces the risk of breaches and ensures workloads are protected from the outset.
ClickOps (manual cloud operations) increases the risk of misconfigurations due to human error and significantly slows down delivery times, hampering efficient response to business needs. AWS provides automation tools to streamline maintenance, scaling, and infrastructure management.
Key automation initiatives:
Organizations that invest in automation early reduce operational overhead and improve overall cloud efficiency.
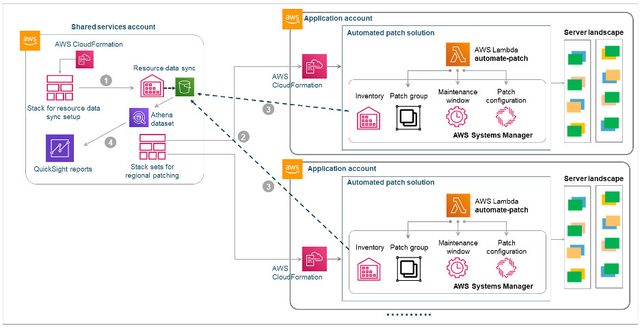
AWS is constantly evolving, with new services, pricing models, and best practices emerging regularly. Companies that embrace a continuous improvement approach to cloud gain a significant competitive edge through enhanced operational efficiency, accelerated innovation, reduced costs, and superior performance—driving greater business agility and market responsiveness.
Ongoing optimization strategies:
Long-term cloud success depends on organizations proactively refining their AWS environment instead of reacting to inefficiencies.
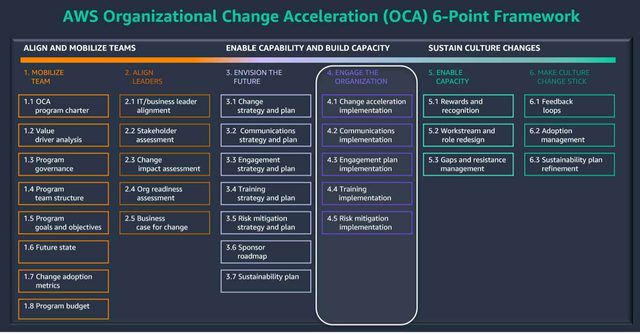
The migration process doesn’t end when workloads are deployed in AWS. The first 90 days post-migration set the stage for long-term performance, cost efficiency, security, and operational maturity.
Organizations that actively monitor workloads, enforce cost controls, strengthen security, automate key tasks, and commit to continuous improvement are far more likely to achieve the full benefits of AWS.
UTurn Data Solutions specializes in helping organizations develop their cloud migration strategy and optimizing their AWS environments post-migration. Whether you need support with cost reduction, security hardening, automation or performance tuning, our team of cloud experts can guide you through the critical first 90 days and beyond.
Schedule a post-migration assessment today: Contact Us

blog
Tools and scripts to help you reclaim your focus and speed up your workflow.
Read More

press release
UTurn Data Solutions achieves the AWS AI Competency, reinforcing its leadership in enterprise AI, data foundations, and AWS innovation.
Read More

press release
Chicago-based AWS consulting partner earns Premier Tier Services designation, recognizing deep cloud, data, and AI expertise and a proven track record helping customers modernize and innovate on AWS.
Read More