Author: Paul Kurzawinski, Cloud Engineer
AWS DRS continuously replicates all configured source servers to AWS account, without any impact on the performance of the source servers. In case of any issue or unexpected downtime, the application can be recovered on AWS within minutes. During recovery, it is possible to pick up the most up-to-date server state as a recovery point or choose to recover an operational copy of your applications from an earlier point in time. Point in time recovery is helpful for recovery from data corruption events such as ransomware. After issues are resolved in your primary environment, you can use AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery to fail back your recovered applications.
Getting Started
From the high-level perspective and operational standpoint, the configuration of AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery (AWS DRS) consist of the following steps:
- Initial configuration – Setting up DRS must be first initialized in the target AWS region by creating the standard replication settings. This will create the required IAM permissions on AWS account.
- Planning – Before setting up AWS DRS, it is crucual to assess your organization’s disaster recovery needs. This includes Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). This will help determine the appropriate AWS DRS configuration for your business.
- Replication Method – AWS DRS supports various replication methods, such as asynchronous and synchronous replication, and continuous data protection. Depending on requirements, you can choose the most suitable replication method for your workloads.
- Settings definition – Once you have selected the replication method, the next step is to configure replication settings in AWS DRS. This involves adding the definition of the replication schedules, target locations and recovery points to ensure data consistency.
- Validation – After setting up replication, it is crucial to test the configuration to ensure that data is being replicated properly and can be easily recovered in case of a disaster. Regular testing and validation are essential to maintain and ensure the effectiveness of AWS DRS setup.
- Monitoring – Verifying the replication status and performance of AWS DRS setup is important to spot any potential failures or misconfiguration. Performing regular maintenance and updates are necessary to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the whole setup.
Overall, the configuration of AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery (AWS DRS) involves careful planning, selection of replication methods, setting up replication, testing, monitoring, and maintenance to ensure the successful implementation of a disaster recovery solution on AWS.
Implementation
To use AWS DRS, it needs to be set up in each AWS Region in which we want to use it (the AWS Region into which the replication is set, and where the Recovery instances will run). Setting up the DRS service needs a default replication setting and roles and permissions required for the service to run and operate.
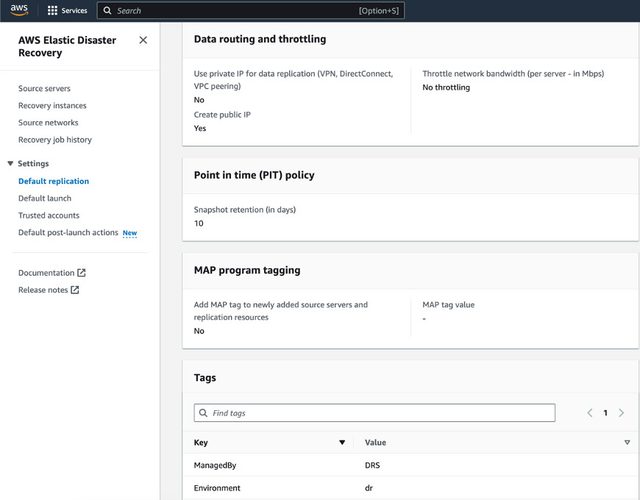
The first step for setting up DRS after activating it and enabling is setting the default replication settings. Choose Set default replication settings on the AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery landing page (screenshot #1 below).